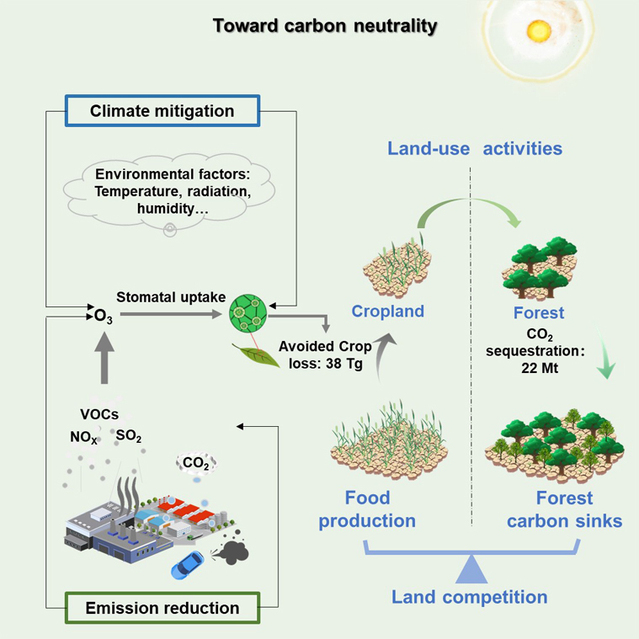
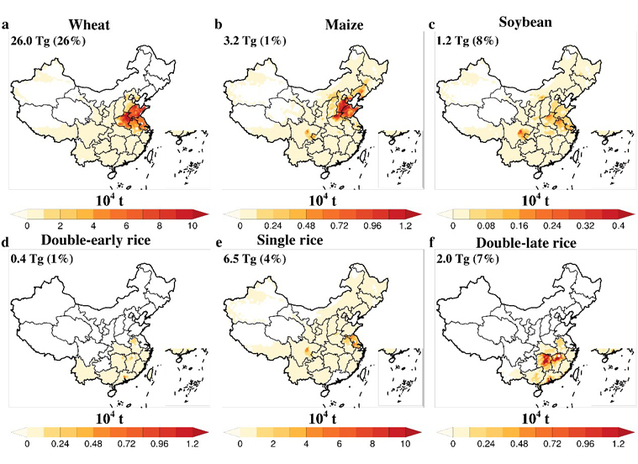
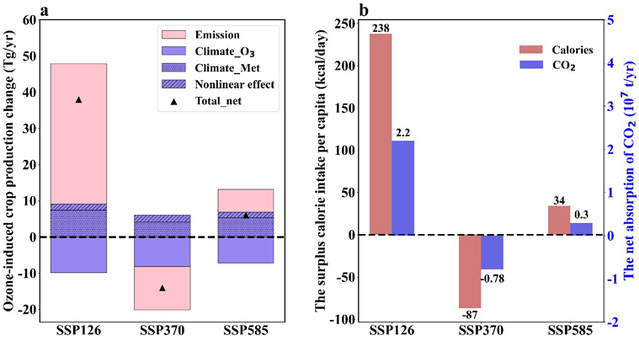
On December 27, 2024, the research team led by Professor Gao Huiwang from the Frontiers Science Center for Deep Ocean Multispheres and Earth System, published their research paper titled Mitigating climate change and ozone pollution will improve Chinese food security in the internationally renowned journal One Earth. Based on an improved dynamical downscaling method, this study applied global models to provide boundary fields that drive regional models, and conducted numerical simulations under various climate change scenarios. It revealed the significance of reducing ozone concentrations in China against the backdrop of carbon neutrality, as well as its importance for enhancing food security and increasing carbon sinks.
Taking into account the regulation of multiple environmental factors, this study identified he impact of the degree of stomatal opening and closing in plant leaves and ozone concentration on the absorption of ozone by crops and the consequent reduction in grain yield. It revealed the significance of mitigating climate change and ozone pollution for food security, and highlighted their important roles in alleviating land competition and global warming. The research further estimated the possible increase in carbon sinks resulting from the partial conversion of farmland to forest. It has provided a significant scientific basis for alleviating air pollution, ensuring food security, and increasing carbon sinks in China.